Tools & Techniques
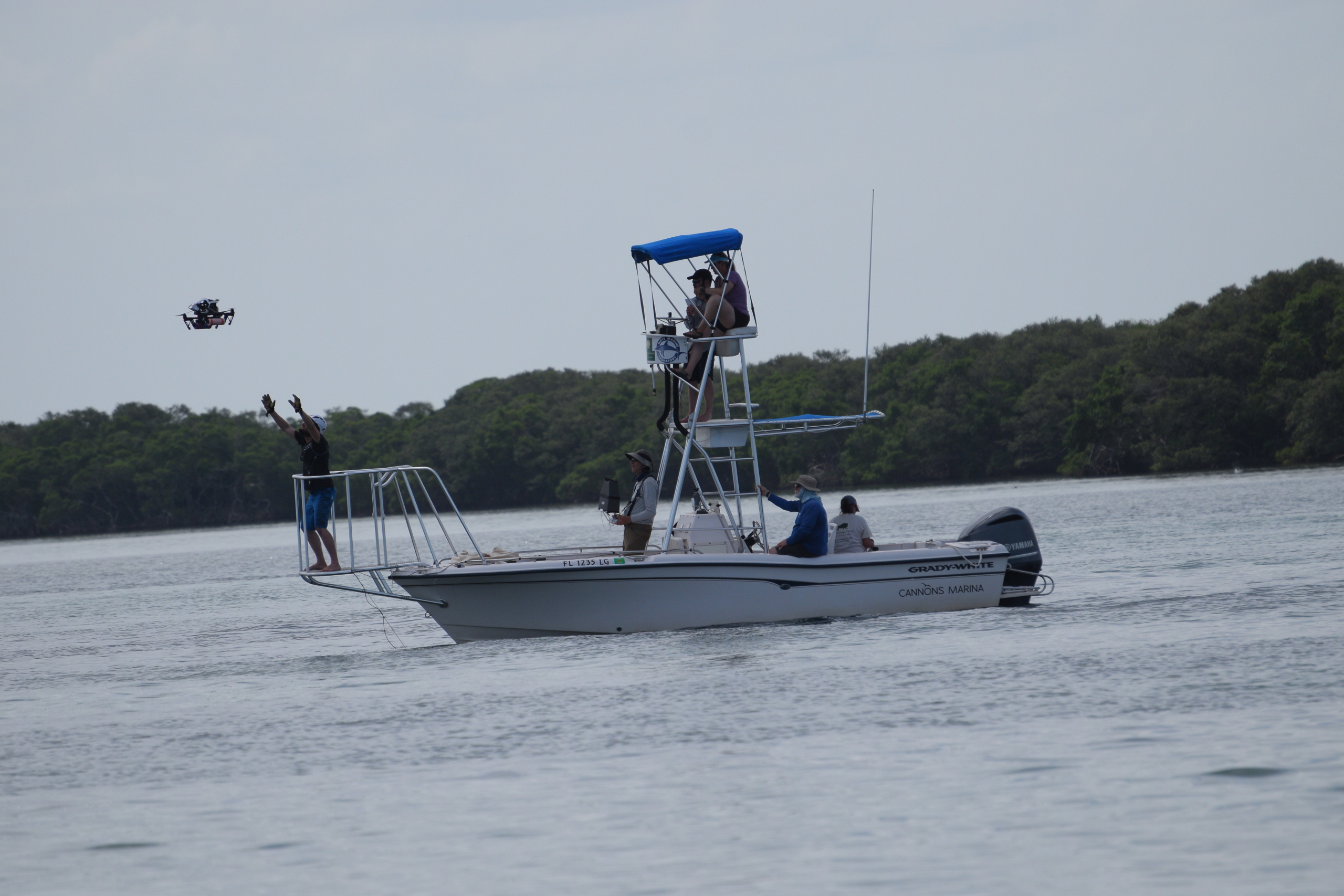

Understanding how dolphins react to disturbances (like boats) is one aspect of behavior we study. Most recently, we’ve employed the use of drones in this research conducted in conjunction with colleagues from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI). Please don’t try this at home: We have special permits that allow us to use drones to study dolphins without harassing them. So please don’t try it on your own!
SDRP conducts the world’s longest-running study of a wild dolphin population, initiated in 1970. Information available from five decades of research on the multi-decadal, multi-generational, year-round resident community of individually identifiable bottlenose dolphins of Sarasota Bay established this as a unique natural laboratory for learning about the biology, behavior, ecology, social structure, health, and communication of dolphins, as well as the effects of human activities on them.
Long-term study is crucial for understanding the lives of members of long-lived species such as bottlenose dolphins, and for being able to detect trends in populations relative to changes in their environment. Knowing the long-term geographic range of a population unit allows the measurement of exposure to threats, which in turn facilitates mitigation, including direct interventions.
The ability to observe identifiable individual dolphins of known sex, age, and familial relationships through all of their life history milestones and associated transitions in behavioral and social patterns, to collect data on health and condition, and to then document their reproductive success and cause of death is rare in cetacean research.
This ability to closely monitor individuals also creates opportunities to develop and refine new research approaches and tools.
The SDRP has acted as a testbed for the development of many innovative methods to study marine mammals. The capture-release health assessments make it possible to attach gear to wild dolphins in a safe and controlled setting and also test the efficacy of things like performing ultrasounds in the field. Innovations occur in medical and veterinary research, as well as studies of dolphin behavior and communication.
Since 1975, Sarasota Bay has been used extensively for testing electronic tags, including radio-tags and satellite-linked tags, for tracking the movements and behavior of dolphins, leading to the very small transmitters used widely today. Digital acoustic archival tags (DTAGs), attached by suction cups for <24 hrs, were developed through tests of bottlenose dolphins in Sarasota Bay, providing a tool for studying communication in free-ranging dolphins, as well as responses to acoustic playbacks and boat approaches.
Data are collected through a variety of techniques, including systematic photographic identification surveys, focal animal behavioral observations, tagging and tracking, and passive acoustic monitoring from shore-based listening stations. Research is conducted under a series of Scientific Research Permits issued by NOAA’s National Marine Fisheries Service, and annual renewals of Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee approvals by Mote Marine Laboratory.
TADpoles and Dolphins
What do TADpoles have to do with dolphins? Development of a remote Tag Attachment Device on a pole. The Sarasota Dolphin Research Program has acted as a testbed for the
Offshore Research Update
June 2024 Offshore Dolphin Research Update Since 2022, we’ve been conducting health assessments of offshore dolphins to gather data needed to address critical information gaps for the little-known species that regularly inhabit west
Eye in the Sky
Using Aerial Drones for Dolphin Research SDRP has a long history of taking to the skies to study dolphins. In the 1990s and early 2000s, a video camera suspended from
Understanding Offshore Dolphin Behavior
High-resolution data-loggers reveal fine-scale movement and foraging behavior of offshore dolphins “Bill,” an Atlantic spotted dolphin, with a satellite-linked tag on his dorsal fin and DTAG on his back upon release in September
Notes from the Lab and Field
This Atlantic spotted dolphin nicknamed Hannah was tagged 45 miles offshore of Sarasota using a new tool we developed. New Tagging Technique Developed in Sarasota Could Impact Dolphins Worldwide If you’ve
Understanding Animal Residency
What is animal residency and how do we define and measure it? In marine mammal research, residency is often used to describe the place that animals (or groups of animals) occupy in a given
Fatty Acid Signatures
If they are what they eat, what are dolphins eating? Thanks to our long-term studies — including seasonal fish surveys — we know what the most common prey fish are in Sarasota Bay dolphin
Taking Lessons From Sarasota Abroad
This 2008 photo shows researchers preparing to release a tagged franciscana dolphin in Argentina. Dolphins were held for a brief period while satellite-linked tags were applied and then the dolphins were released on site.
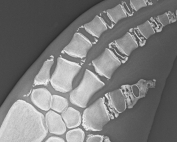
Using X-Rays to Estimate Dolphin Age
X-ray images (radiographs) of human hands have been used for decades as a method of confirming age by examining the predictable chronological changes occurring to the growth plates of each bone. We wanted to know if
The Bottlenose Epigenetic Aging Tool (BEAT)
We're working to create a Bottlenose Epigenetic Aging Tool (BEAT) that will allow us to use small skin samples to determine the age of dolphins. First, what is epigenetics? These are various modifications and molecules